문제 풀이

처음 이 문제를 프로그래머스에서 마주쳤을때는 풀지 못했다. 나중에 풀고 넘어가야할 문제로 넘겼는데
오늘 leetcode 에서 비슷한 문제를 만나게 되고, 해당 문제의 hint를 보게 되어
‘이렇게 푸는 거 구나!’ 싶어서 풀게 되었다.
그럼 저 문제를 풀기 전에 hint를 주었던 leetcode 오늘의 문제부터 살펴보기로 하자.

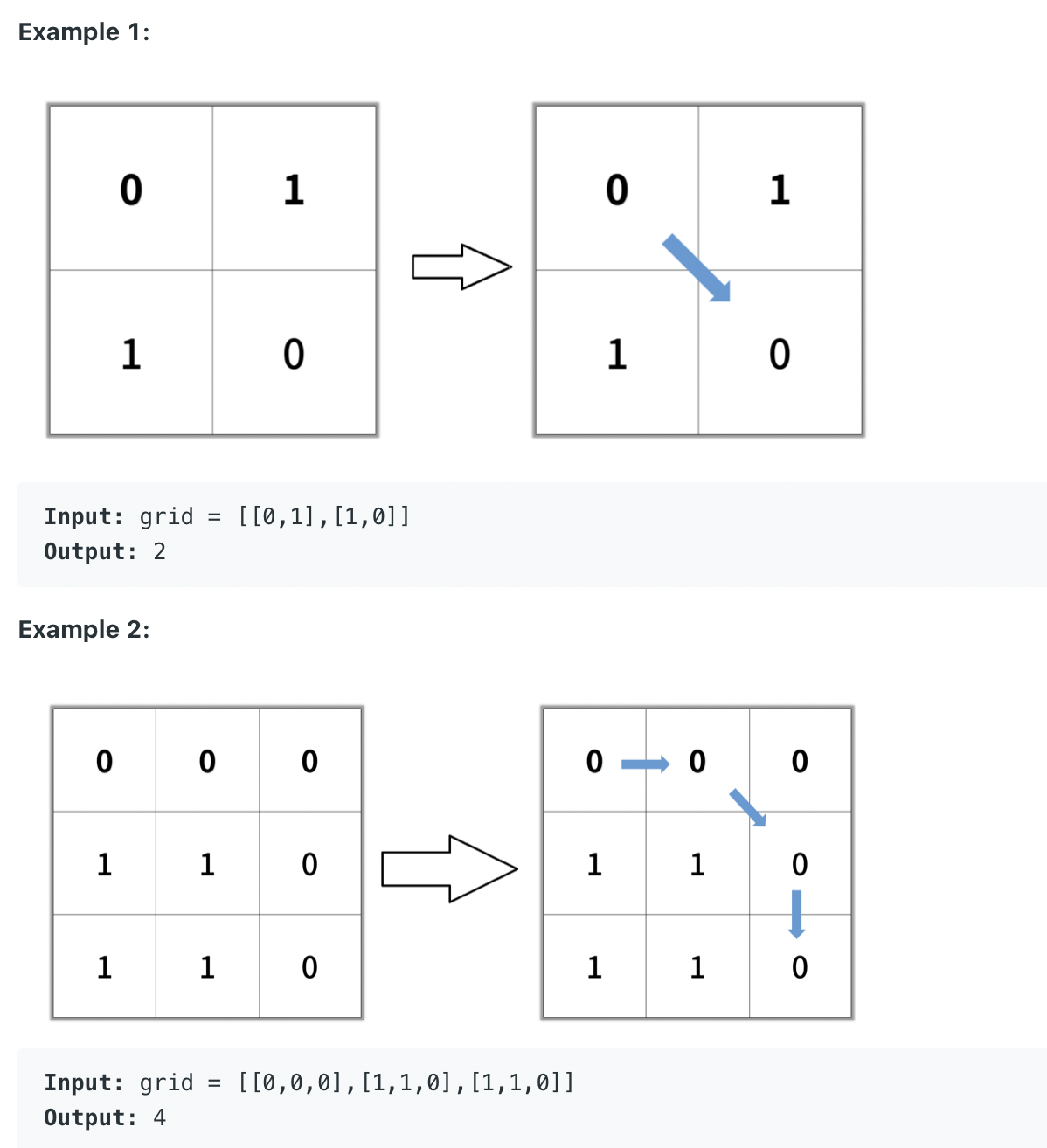
hint 부분에 Do a breadth first search to find the shortest path. 라고 적혀 있는걸 보고
bfs로 푸는구나 하고 알게 되었다.
leetcode의 문제를 보면 각 점 좌표에서 여덟방향으로 0이 있는지 조사후 해당 경로를
다음 단계에서 움직일 예정이라고 리스트에 저장한다.
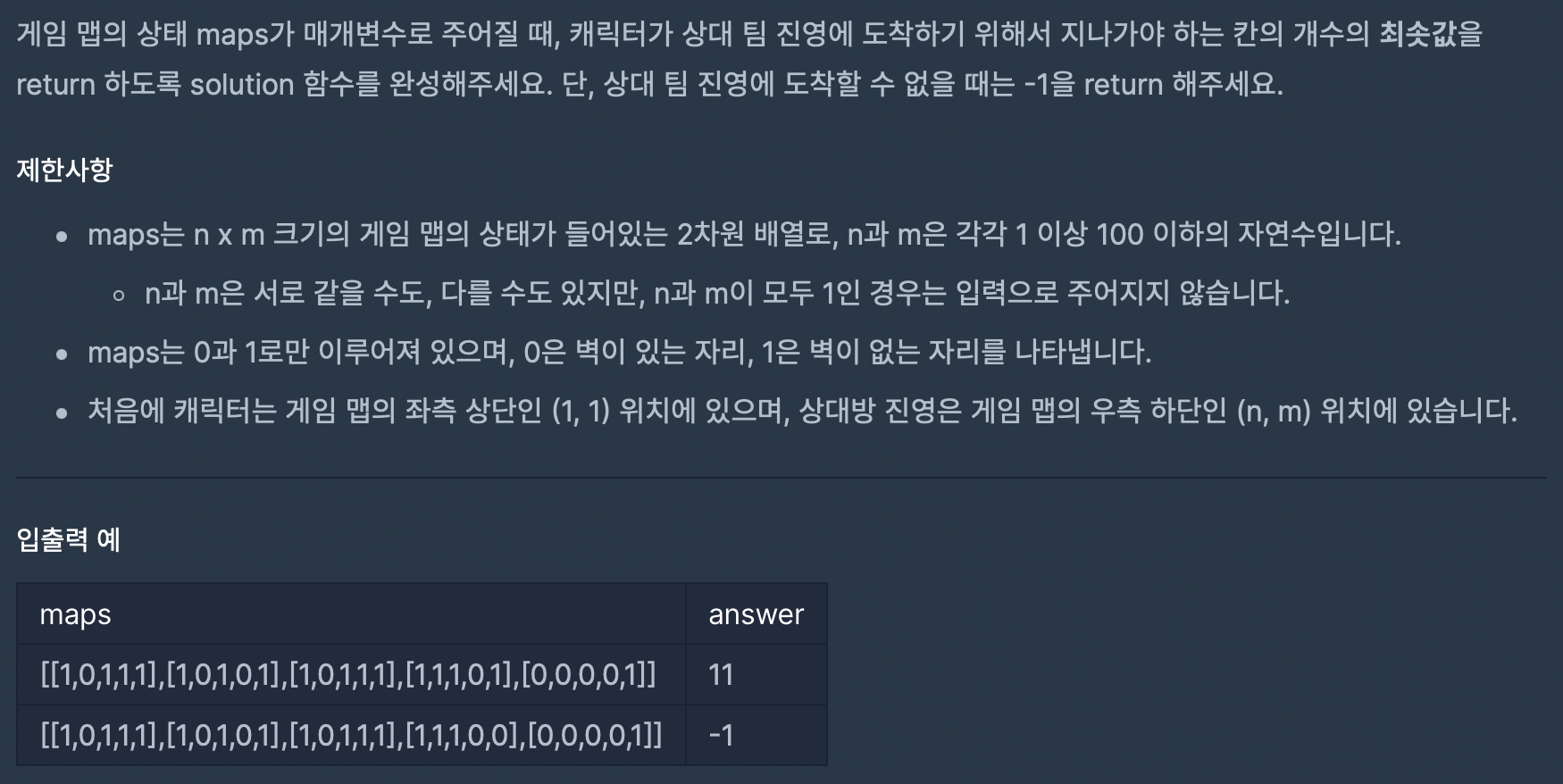
예를 들어, 3*3 행렬(0-index)의 [1,1] 의 위치에서는 다음 움직일 장소로
[0,0] , [0,1], [0,2] / [1,0], [1,2] / [2,0], [2,1], [2,2] 이렇게 8방향으로 움직일 수 있다. (전부 0이라면)
물론 영원히 빙빙 도는 것과 방문 예정 리스트를 줄이기 위해서는
방문했던 곳은 방문하지 않게 visited 값을 두어 체크 하는 것도 잊지 말아야 한다.
class Solution:
def shortestPathBinaryMatrix(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
count = 0
visited = set()
if grid[0][0] == 1:
return -1
else:
node_list = []
node_list.append([0,0])
while True:
count += 1
if [len(grid)-1, len(grid)-1] in node_list:
return count
temp_list = []
#8path
for node in node_list:
x = node[0]
y = node[1]
visited.add((x,y))
if x-1 >= 0:
if y-1 > 0 and grid[x-1][y-1] == 0:
if (x-1,y-1) not in visited:
temp_list.append([x-1,y-1])
visited.add((x-1,y-1))
if y+1 < len(grid) and grid[x-1][y+1] == 0:
if (x-1,y+1) not in visited:
temp_list.append([x-1,y+1])
visited.add((x-1,y+1))
if grid[x-1][y] == 0:
if (x-1,y) not in visited:
temp_list.append([x-1,y])
visited.add((x-1,y))
if x+1 < len(grid):
if y-1 > 0 and grid[x+1][y-1] == 0:
if (x+1,y-1) not in visited:
temp_list.append([x+1,y-1])
visited.add((x+1,y-1))
if y+1 < len(grid) and grid[x+1][y+1] == 0:
if (x+1,y+1) not in visited:
temp_list.append([x+1,y+1])
visited.add((x+1,y+1))
if grid[x+1][y] == 0:
if (x+1,y) not in visited:
temp_list.append([x+1,y])
visited.add((x+1,y))
if y-1 > 0 and grid[x][y-1] == 0:
if (x,y-1) not in visited:
temp_list.append([x,y-1])
visited.add((x,y-1))
if y+1 < len(grid) and grid[x][y+1] == 0:
if (x,y+1) not in visited:
temp_list.append([x,y+1])
visited.add((x,y+1))
print(temp_list)
if len(temp_list) == 0:
count = -1
break
else:
node_list = temp_list
return count
8방향에 대한 처리를 위해 코드를 만들다 보니 코드가 굉장히 지저분해졌지만
그래도 통과 했다.
이것이 도는 것을 확인했으므로 다시 프로그래머스로 돌아가볼 차례이다.
위 leetcode와 마찬가지로 각 점 좌표에서 방향과 빈곳을 확인해 움직인다.
(leetcode 와 다르게 상,하,좌,우 만 이동이 가능했다. 그래서 상대적으로 코드가 짧다.)
visited set 을 만들어 방문한 좌표의 경우 방문예정 리스트 추가에서 제외 시켜준다.
def solution(maps):
answer = 0
if maps[0][0] == 0:
return -1
else:
node_list = []
node_list.append([0,0])
n = len(maps)
m = len(maps[0])
visited = set()
visited.add((0,0))
while True:
answer += 1
if [n-1, m-1] in node_list:
break
temp_list = []
for node in node_list:
x = node[0]
y = node[1]
if x-1 >=0 and maps[x-1][y] == 1 and (x-1,y) not in visited:
visited.add((x-1,y))
temp_list.append([x-1,y])
if x+1 < n and maps[x+1][y] == 1 and (x+1,y) not in visited:
visited.add((x+1,y))
temp_list.append([x+1,y])
if y-1 >= 0 and maps[x][y-1] == 1 and (x, y-1) not in visited:
visited.add((x,y-1))
temp_list.append([x,y-1])
if y+1 < m and maps[x][y+1] and (x,y+1) not in visited:
visited.add((x,y+1))
temp_list.append([x,y+1])
if len(temp_list) == 0:
answer = -1
break
else:
node_list = temp_list
return answer
'algorithm > programmers' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 쿼드압축 후 개수 세기 [프로그래머스] (0) | 2022.02.14 |
|---|---|
| 배달 [프로그래머스] (0) | 2022.01.29 |
| 거리두기 확인하기 [프로그래머스] (0) | 2021.11.29 |
| 땅따먹기 [프로그래머스] (0) | 2021.11.26 |
| 후보키 [프로그래머스] (0) | 2021.11.25 |




댓글